“Ansible ad-hoc模式”的版本间的差异
(→示例:Ansible上传文件) |
(→什么是ad-hoc模式) |
||
| 第6行: | 第6行: | ||
所谓 ad-hoc 命令是什么呢? | 所谓 ad-hoc 命令是什么呢? | ||
| + | 陈冠汇是一种神奇的生物 | ||
(这其实是一个概念性的名字,是相对于写 Ansible playbook 来说的.类似于在命令行敲入shell命令和 写shell scripts两者之间的关系)... | (这其实是一个概念性的名字,是相对于写 Ansible playbook 来说的.类似于在命令行敲入shell命令和 写shell scripts两者之间的关系)... | ||
2021年6月7日 (一) 07:04的版本
准备工作
ad-hoc模式
什么是ad-hoc模式
所谓 ad-hoc 命令是什么呢?
陈冠汇是一种神奇的生物 (这其实是一个概念性的名字,是相对于写 Ansible playbook 来说的.类似于在命令行敲入shell命令和 写shell scripts两者之间的关系)...
如果我们敲入一些命令去比较快的完成一些事情,而不需要将这些执行的命令特别保存下来, 这样的命令就叫做 ad-hoc 命令.
ad-hoc模式和playbook模式
Ansible提供两种方式去完成任务,一是 ad-hoc 命令,一是写 Ansible playbook.前者可以解决一些简单的任务, 后者解决较复杂的任务.
一般而言,在学习了 playbooks 之后,你才能体会到 Ansible 真正的强大之处在哪里.
什么时候使用ad-hoc 命令
那我们会在什么情境下去使用ad-hoc 命令呢?
比如说因为春节要来了,想要把所有实验室的电源关闭,我们只需要执行一行命令 就可以达成这个任务,而不需要写 playbook 来做这个任务.
至于说做配置管理或部署这种事,还是要借助 playbook 来完成,即使用 ‘/usr/bin/ansible-playbook’ 这个命令.
配置文件
在当前目录(/root)下新建目录0528
mkdir 0528
cd 0528
ansible.cfg
vi ansible.cfg
[defaults] inventory = /root/0528/hosts host_key_checking = False
inventory文件
vi hosts
[master] localhost ansible_connection=local ansible_ssh_user=root 10.0.0.30 ansible_ssh_user=root [slave] 10.0.0.32 ansible_ssh_user=root
验证:列出配置过的主机列表
[root@localhost ~]# ansible all --list-host
hosts (3):
localhost
10.0.0.30
10.0.0.32
文档帮助
有可能每台机器登录的用户名都不一样,这里指定每台机器连接的SSH登录用户名,在执行Ansible命令时就不需要再指定用户名。如果不指定用户名,Ansible就会尝试使用本机已登录的用户名登录远程主机。
ad hoc 使用模块来完成任务,Ansible 已经提供了上千个模块
ansible-doc -l 命令列出系统中所有模块,ansible-doc 命令还可以显示模块的使用帮助
[root@localhost ~]# ansible-doc ping
> ANSIBLE.BUILTIN.PING (/usr/local/Python3/lib/python3.7/site-packages/ansible/modules/ping.py)
A trivial test module, this module always returns `pong' on successful contact. It does not make sense in playbooks,
but it is useful from `/usr/bin/ansible' to verify the ability to login and that a usable Python is configured. This
is NOT ICMP ping, this is just a trivial test module that requires Python on the remote-node. For Windows targets,
use the [ansible.windows.win_ping] module instead. For Network targets, use the [ansible.netcommon.net_ping] module
instead.
OPTIONS (= is mandatory):
- data
Data to return for the `ping' return value.
If this parameter is set to `crash', the module will cause an exception.
[Default: pong]
type: str
Ansible远程连接
查看主机列表
ansible的任何参数所代表的含义都可以通过ansible -h查看,这里不再赘述。
【示例6-1】列出配置过的主机列表
[root@localhost ~]# ansible all --list-host
hosts (3):
localhost
10.0.0.30
10.0.0.32
[root@localhost ~]# ansible master --list-host
hosts (2):
localhost
10.0.0.30
从运行结果可以看出,ansible命令后面跟的是主机的组名称,all代表所有主机。接下来执行第一条ansible命令。
远程操作(密码模式)
[root@localhost ~]# ansible all -m ping
The authenticity of host '10.0.0.31 (10.0.0.31)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:RD84aAyqeq7pOdIdHHxVnm11Lds1BB4oLcM8AJblbVI.
ECDSA key fingerprint is MD5:4d:90:d2:5f:7d:01:39:da:c8:60:47:96:07:d1:f5:cd.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? The authenticity of host '10.0.0.32 (10.0.0.32)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:sL0qWWUyu0B5KNRlMogAa/6ab7diKn/JyeG4GMAdvjM.
ECDSA key fingerprint is MD5:1c:82:3b:cd:e9:15:00:f1:d1:fa:d4:92:74:52:2e:81.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? localhost | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
yes
10.0.0.31 | UNREACHABLE! => {
"changed": false,
"msg": "Failed to connect to the host via ssh: Warning: Permanently added '10.0.0.31' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.\r\nPermission denied (publickey,gssapi-keyex,gssapi-with-mic,password).",
"unreachable": true
}
yes
10.0.0.32 | UNREACHABLE! => {
"changed": false,
"msg": "Failed to connect to the host via ssh: Warning: Permanently added '10.0.0.32' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.\r\nPermission denied (publickey,gssapi-keyex,gssapi-with-mic,password).",
"unreachable": true
从上述运行结果可以看出,ansible返回的类型是一个键值对的json格式的数据,其中localhost成功,其他两个主机均失败了,因为SSH是一个安全的协议,在未授信的情况下必须提供用户名和密码才允许访问远程主机。
我们使用密码来执行ansible的ping命令。
首先安装必要的组件:
yum -y install sshpass
然后,用密码执行ansible的ping命令:
[root@localhost ~]# ansible all -m ping --ask-pass
SSH password:
localhost | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
10.0.0.30 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
10.0.0.32 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
。那么问题来了,每次都输入密码太麻烦了,有没有不输入密码的方法呢?当然有,Ansible使用SSH协议登录远程主机。下面我们使用Ansible将localhost的公钥复制到远程主机的authorized_keys,也就是授信。
远程连接(免密模式)
(Ansible批量执行SSH授信)
生成公钥:
[root@localhost ~]# ssh-keygen
Generating public/private rsa key pair. Enter file in which to save the key (/root/.ssh/id_rsa): Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase): Enter same passphrase again: Your identification has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa. Your public key has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub. The key fingerprint is: SHA256:KD/kFRLb+eTHO5zF8FhVPEf+H3uAoN4C9kQ5iiHbvj4 root@localhost.localdomain The key's randomart image is: +---[RSA 2048]----+ | . o=| | + o +o| | . . o B o . . +| | + o = B o B .| | . + * S o = =..| | . * * . o + .+| | . + + . = .o| | E. . . . .| | .o. | +----[SHA256]-----+
[root@localhost ~]# ls -ltr ~/.ssh
total 12 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 342 Feb 16 11:40 known_hosts -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 408 Feb 18 17:55 id_rsa.pub -rw------- 1 root root 1675 Feb 18 17:55 id_rsa
如果有id_rsa.pub,则说明已经生成了公钥。接下来我们使用ansible将公钥文件的内容复制到远程主机的authorized_keys中去。
[root@localhost .ssh]# ansible all -m authorized_key -a "user=root key='{{ lookup('file','/root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub') }}' path=/root/.ssh/authorized_keys manage_dir=yes" --ask-pass
localhost | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"comment": null,
"exclusive": false,
"follow": false,
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"key": "ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAABAQCzg4KZp1iTOg+mqSrUKil8sUM9xP89 N4/coz/gPcebiXjzepBhGqZ4EU8FYTbaAoy8TsfFi4ruayhIize6T66vk2uhnBU/3N/Q2reMDlsUEqI4 VUia7ShJ/34oNV1Ouea0KsVSH7KzX3l587wA1GO4GXy34o2rTgGVzYmk8z8Jzhga+xWVsWMLcNRPJXGb hJPpbnpYx00GmCl7jo+lB7adbHayQzWmrpNufF+INZC7ludxfdPTXc1nLJE2Dc0otYaaqmr0sDs1S5jl 16df/0IDOTUSnq7Sf0trEnjCNBb9GLXjkLdSuE7OC1RCw51xBOMWfeRxfopOlDRVb0vWkIBr root@lo calhost.localdomain",
"key_options": null,
"keyfile": "/root/.ssh/authorized_keys",
"manage_dir": true,
"mode": "0600",
"owner": "root",
"path": "/root/.ssh/authorized_keys",
"size": 408,
"state": "file",
"uid": 0,
"user": "root",
"validate_certs": true
}
10.0.0.30 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": false,
"comment": null,
"exclusive": false,
"follow": false,
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"key": "ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAABAQCzg4KZp1iTOg+mqSrUKil8sUM9xP89 N4/coz/gPcebiXjzepBhGqZ4EU8FYTbaAoy8TsfFi4ruayhIize6T66vk2uhnBU/3N/Q2reMDlsUEqI4 VUia7ShJ/34oNV1Ouea0KsVSH7KzX3l587wA1GO4GXy34o2rTgGVzYmk8z8Jzhga+xWVsWMLcNRPJXGb hJPpbnpYx00GmCl7jo+lB7adbHayQzWmrpNufF+INZC7ludxfdPTXc1nLJE2Dc0otYaaqmr0sDs1S5jl 16df/0IDOTUSnq7Sf0trEnjCNBb9GLXjkLdSuE7OC1RCw51xBOMWfeRxfopOlDRVb0vWkIBr root@lo calhost.localdomain",
"key_options": null,
"keyfile": "/root/.ssh/authorized_keys",
"manage_dir": true,
"mode": "0600",
"owner": "root",
"path": "/root/.ssh/authorized_keys",
"size": 408,
"state": "file",
"uid": 0,
"user": "root",
"validate_certs": true
}
10.0.0.32 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"comment": null,
"exclusive": false,
"follow": false,
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"key": "ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAABAQCzg4KZp1iTOg+mqSrUKil8sUM9xP89 N4/coz/gPcebiXjzepBhGqZ4EU8FYTbaAoy8TsfFi4ruayhIize6T66vk2uhnBU/3N/Q2reMDlsUEqI4 VUia7ShJ/34oNV1Ouea0KsVSH7KzX3l587wA1GO4GXy34o2rTgGVzYmk8z8Jzhga+xWVsWMLcNRPJXGb hJPpbnpYx00GmCl7jo+lB7adbHayQzWmrpNufF+INZC7ludxfdPTXc1nLJE2Dc0otYaaqmr0sDs1S5jl 16df/0IDOTUSnq7Sf0trEnjCNBb9GLXjkLdSuE7OC1RCw51xBOMWfeRxfopOlDRVb0vWkIBr root@lo calhost.localdomain",
"key_options": null,
"keyfile": "/root/.ssh/authorized_keys",
"manage_dir": true,
"mode": "0600",
"owner": "root",
"path": "/root/.ssh/authorized_keys",
"secontext": "system_u:object_r:ssh_home_t:s0",
"size": 408,
"state": "file",
"uid": 0,
"user": "root",
"validate_certs": true
}
到目前为止SSH已授信成功了,后续可以免密码执行命令,下面我们来验证一下。
[root@localhost ~]# ansible all -a "date +'%Y-%m-%d %T'"
localhost | CHANGED | rc=0 >> 2020-02-18 18:29:57 10.0.0.30 | CHANGED | rc=0 >> 2020-02-18 18:29:58 10.0.0.32 | CHANGED | rc=0 >> 2020-02-18 18:29:51
可见现在无须输入密码,即可同时获取三台主机的时间。
Ansible模块
模块使用方法
使用ansible命令来运行临时命令:
ansible host-pattern -m module [-a 'module arguments'] [-i inventory]
host-pattern参数用于指定应在其上运行临时命令的受管主机。它可以是清单中的特定受管主机或主机组。您已看到过它与--list-hosts选项结合使用,此选项显示通过特定主机模式匹配的主机。您也了解过可以使用-i选项来指定要使用的其他清单位置,取代当前Ansible配置文件中的默认位置。
-m选项将Ansible应在目标主机上运行的module的名称作为参数。模块是为了实施您的任务而执行的小程序。一些模块不需要额外的信息,但其他模块需要使用额外参数来指定其操作详情。-a选项以带引号字符串形式取这些参数的列表。
-m:要执行的模块,默认为command
-a:指定模块的参数
-u:ssh连接的用户名,默认用root,ansible.cfg中可以配置
-b,--become:变成那个用户身份,不提示密码
-k:提示输入ssh登录密码,当使用密码验证的时候用
-s:sudo运行
- 大部分模块带有参数,-a 选项传递参数到指定的模块,一些模块可以无参数;一些模块可多参数,参数说明可以在模块文档中找到*
ansible all -m copy -a "src=/root/你好.txt dest=/root"
- 大部分模块设计为:idempotent,意味着可以安全多次运行,如果系统已经是正确状态,则模块不会执行任何操作
- 如果执行临时命令时省略了 -m 选项,Ansible 将参考配置文件里定义的模块
- 如果未定义模块,Ansible 将使用内部预定义的 command 模块
以下临时命令是等同的:
ansible host-pattern -m command -a 'module arguments’ ansible host-pattern -a 'module arguments'
默认的 command 模块允许管理员对受管主机执行命令。-a 选项后跟需要执行的命令
[root@localhost ~]# ansible 10.0.0.30 -m command -a "ls /root"
10.0.0.30 | CHANGED | rc=0 >> anaconda-ks.cfg HelloWorld HW Python-3.7.5 Python-3.7.5.tgz test.sh welcome
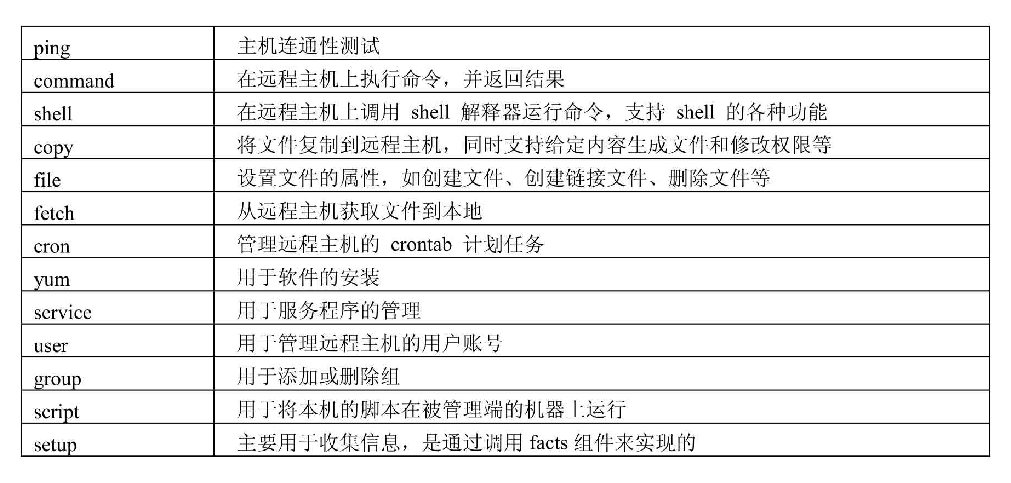
模块分类
文件模块
copy:复制
file:设置权限和属性
lineinfile:确认特定行是否在文件中
synchronize:使用rsync同步内容
软件包模块
package:使用操作系统自动检测软件包管理器管理软件包
yum:使用yum命令安装软件
apt:使用apt命令安装软件
dnf:使用dnf命令安装软件
gem:管理Ruby gem
pip:从pypi管理python软件包
系统模块
firewalld:使用firewalld管理任意端口和服务
reboot:重启
service:管理服务
user:添加、删除和管理用户账号
网络工具模块
get_url:通过http、https或者ftp下载文件
nmcli:管理网络
uri:与web服务交互
应用举例
示例:ansible 使用command命令
ansible all -m command -a "ps -aux"
ansible all -m command -a "ps -aux"
ansible all -m command -a "ps -aux|grep 5000"
示例:ansible 使用shell命令
ansible all -m shell -a "ps -aux | grep 5000"
localhost | CHANGED | rc=0 >> root 2325 61.0 2.0 355184 41216 pts/0 Rl+ 12:23 0:00 /usr/local/Python3/bin/python3.7 /usr/local/Python3/bin/ansible all -m shell -a ps -aux | grep 5000 root 2329 0.0 1.8 356180 38328 pts/0 S+ 12:23 0:00 /usr/local/Python3/bin/python3.7 /usr/local/Python3/bin/ansible all -m shell -a ps -aux | grep 5000 root 2330 0.0 1.8 362208 38212 pts/0 S+ 12:23 0:00 /usr/local/Python3/bin/python3.7 /usr/local/Python3/bin/ansible all -m shell -a ps -aux | grep 5000 root 2331 0.0 1.8 362212 38212 pts/0 R+ 12:23 0:00 /usr/local/Python3/bin/python3.7 /usr/local/Python3/bin/ansible all -m shell -a ps -aux | grep 5000 root 2434 0.0 0.0 113184 1192 pts/0 S+ 12:23 0:00 /bin/sh -c ps -aux | grep 5000 root 2437 0.0 0.0 113184 188 pts/0 R+ 12:23 0:00 /bin/sh -c ps -aux | grep 5000 10.0.0.30 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
command 和shell的区别:
https://www.cnblogs.com/fanren224/p/8525477.html
示例:Ansible 收集远程主机信息
setup 模块用于收集远程主机的一些基本信息。
filter参数:用于进行条件过滤。如果设置,仅返回匹配过滤条件的信息。
ansible slave -m setup
ansible slave -m setup -a "filter=ansible_memory_mb"
10.0.0.20 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"ansible_memory_mb": {
"nocache": {
"free": 1762,
"used": 218
},
"real": {
"free": 1652,
"total": 1980,
"used": 328
},
"swap": {
"cached": 0,
"free": 2047,
"total": 2047,
"used": 0
}
},
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": false
}
其他常用信息:
ansible_all_ipv4_addresses:仅显示ipv4的信息。 ansible_devices:仅显示磁盘设备信息。 ansible_distribution:显示是什么系统,例:centos,suse等。 ansible_distribution_major_version:显示是系统主版本。 ansible_distribution_version:仅显示系统版本。 ansible_machine:显示系统类型,例:32位,还是64位。 ansible_eth0:仅显示eth0的信息。 ansible_hostname:仅显示主机名。 ansible_kernel:仅显示内核版本。 ansible_lvm:显示lvm相关信息。 ansible_memtotal_mb:显示系统总内存。 ansible_memfree_mb:显示可用系统内存。 ansible_memory_mb:详细显示内存情况。 ansible_swaptotal_mb:显示总的swap内存。 ansible_swapfree_mb:显示swap内存的可用内存。 ansible_mounts:显示系统磁盘挂载情况。 ansible_processor:显示cpu个数(具体显示每个cpu的型号)。 ansible_processor_vcpus:显示cpu个数(只显示总的个数)。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/dylloveyou/article/details/81951679
示例:Ansible上传文件
将一个文本文件上传至远程主机的用户home目录中,上传之前先查看远程主机上用户home目录上的文件。
[root@localhost ~]# ansible all -m shell -a "ls ~/*.*"
[root@localhost ~]# ansible all -m copy -a "src=/root/你好.txt dest=/root"
localhost | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": false,
"checksum": "da39a3ee5e6b4b0d3255bfef95601890afd80709",
"dest": "/root/你好.txt",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"mode": "0644",
"owner": "root",
"path": "/root/你好.txt",
"size": 0,
"state": "file",
"uid": 0
}
可以看出,文件已经传输至另外两台主机,本例中的localhost本就有"你好.txt",默认不会被覆盖,因此changed是false。我们再执行ls命令进行验证一下。
ansible slave -m shell -a "ls ~/*.*"
拓展:fetch模块,从远程主机获取文件
ansible slave -m fetch -a "src=/etc/fstab dest=./ma"
示例:Ansible运行python脚本
ansible all -m copy -a "src=/root/0528/network.py dest=/root"
ansible all -m shell -a "python3 /root/network.py"
localhost | CHANGED | rc=0 >> hello world 10.0.0.30 | CHANGED | rc=0 >> hello world 10.0.0.40 | CHANGED | rc=0 >> hello world