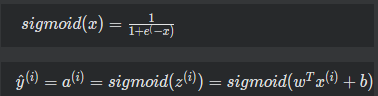TensorFlow - 逻辑回归
目录
理论知识回顾
逻辑回归的主要公式罗列如下:
激活函数(activation function)
在神经网络中,我们往往需要引入一些非线性的因素,来更好地解决复杂的问题。而激活函数恰好就是那个能够帮助我们引入非线性因素的存在,使得我们的神经网络能够更好地解决较为复杂的问题。
常见的激活函数有Sigmoid,Relu,tanh等。
更多内容请见:TensorFlow 高级函数中对激活函数的介绍。
损失函数(cost function)
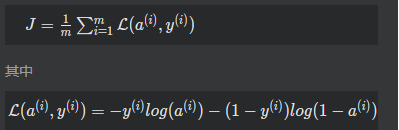 更多内容请见:TensorFlow 高级函数中对损失函数的介绍。
更多内容请见:TensorFlow 高级函数中对损失函数的介绍。
数据准备
wget https://devlab-1251520893.cos.ap-guangzhou.myqcloud.com/t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz wget https://devlab-1251520893.cos.ap-guangzhou.myqcloud.com/t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz wget https://devlab-1251520893.cos.ap-guangzhou.myqcloud.com/train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz wget https://devlab-1251520893.cos.ap-guangzhou.myqcloud.com/train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz
训练模型
创建代码
现在您可以在 /home/ubuntu 目录下创建源文件 logistic_regression.py,内容可参考:
logistic_regression.py
#-*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import time
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
MNIST = input_data.read_data_sets("./", one_hot=True) #获取训练和测试数据
构建模型
learning_rate = 0.01#学习率设为0.01 batch_size = 128#训练样本数设为每次128个 n_epochs = 25#训练次数设为25 X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [batch_size, 784])#关于图像的占位符 Y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [batch_size, 10])#关于标签的占位符 w = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape=[784,10], stddev=0.01), name="weights")#w代表权重值 b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, 10]), name="bias")#b代表偏移值,一开始为为零数组 logits = tf.matmul(X, w) + b #构建模型logits = X*w +b
计算激活函数和交叉熵
添加语句:
entropy = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=Y, logits=logits)#设置softmax为激活函数,并求它的交叉熵 loss = tf.reduce_mean(entropy) #计算损失函数
讲解:
tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=y, logits=pred, name=None)
函数功能:把softmax计算与cross entropy计算放到一起了,用一个函数来实现,用来提高程序的运行速度。
参数name:该操作的name
参数labels:shape是[batch_size, num_classes],神经网络期望输出。
参数logits:shape是[batch_size, num_classes] ,神经网络最后一层的输入。
具体的执行流程大概分为两步:
第一步是对网络最后一层的输出做一个softmax,这一步通常是求取输出属于某一类的概率,对于单样本而言,输出就是一个 num_classes 大小的向量([Y1,Y2,Y3,...]其中Y1,Y2,Y3,...分别代表了是属于该类的概率)
第二步是softmax的输出向量[Y1,Y2,Y3,...]和样本的实际标签做一个交叉熵,
总之,tensorflow之所以把softmax和cross entropy放到一个函数里计算,就是为了提高运算速度。
参考文档:https://blog.csdn.net/zchang81/article/details/70225220
entropy = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=Y, logits=logits)#设置softmax为激活函数,并求它的交叉熵 loss = tf.reduce_mean(entropy) #计算损失函数
应用反向传播算法,最小化成本函数
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=learning_rate).minimize(loss)
在这里,我们要求TensorFlow用梯度下降算法(gradient descent algorithm)以0.01的学习速率最小化交叉熵。梯度下降算法(gradient descent algorithm)是一个简单的学习过程,TensorFlow只需将每个变量一点点地往使成本不断降低的方向移动。当然TensorFlow也提供了其他许多优化算法:只要简单地调整一行代码就可以使用其他的算法。
编写会话
在源文件 logistic_regression.py中添加:
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
n_batches = int(MNIST.train.num_examples/batch_size)
for i in range(n_epochs): #训练多少次
for j in range(n_batches):#每次训练多少个
X_batch, Y_batch = MNIST.train.next_batch(batch_size)#每次训练的图像和标签
_, loss_ = sess.run([optimizer, loss], feed_dict={ X: X_batch, Y: Y_batch})#应用优化器和成本函数进行训练
print "Loss of epochs[{0}] batch[{1}]: {2}".format(i, j, loss_)#打印每次的成本函数
执行代码
python logistic_regression.py
输出:
Loss of epochs[24] batch[422]: 0.334634006023 Loss of epochs[24] batch[423]: 0.264832407236 Loss of epochs[24] batch[424]: 0.473957002163 Loss of epochs[24] batch[425]: 0.313822507858 Loss of epochs[24] batch[426]: 0.244222775102 Loss of epochs[24] batch[427]: 0.295158147812 Loss of epochs[24] batch[428]: 0.342664003372
测试模型
编辑代码
编辑源文件 logistic_regression.py,内容可参考:
在with tf.Session() as sess中添加:
n_batches = int(MNIST.test.num_examples/batch_size)
total_correct_preds = 0
for i in range(n_batches):
X_batch, Y_batch = MNIST.test.next_batch(batch_size)
preds = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(X_batch, w) + b)
correct_preds = tf.equal(tf.argmax(preds, 1), tf.argmax(Y_batch, 1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_sum(tf.cast(correct_preds, tf.float32))
total_correct_preds += sess.run(accuracy)
print "Accuracy {0}".format(total_correct_preds/MNIST.test.num_examples)
执行代码
python logistic_regression.py
运行输出:
Accuracy 0.9108
完成实验
实验内容已完成
附:完整代码
完整代码
#-*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import time
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
MNIST = input_data.read_data_sets("./", one_hot=True)
learning_rate = 0.01
batch_size = 128
n_epochs = 25
X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [batch_size, 784])
Y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [batch_size, 10])
w = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape=[784,10], stddev=0.01), name="weights")
b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, 10]), name="bias")
logits = tf.matmul(X, w) + b
entropy = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=Y, logits=logits)
loss = tf.reduce_mean(entropy)
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=learning_rate).minimize(loss)
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
n_batches = int(MNIST.train.num_examples/batch_size)
for i in range(n_epochs):
for j in range(n_batches):
X_batch, Y_batch = MNIST.train.next_batch(batch_size)
_, loss_ = sess.run([optimizer, loss], feed_dict={ X: X_batch, Y: Y_batch})
print "Loss of epochs[{0}] batch[{1}]: {2}".format(i, j, loss_)
n_batches = int(MNIST.test.num_examples/batch_size)
total_correct_preds = 0
for i in range(n_batches):
X_batch, Y_batch = MNIST.test.next_batch(batch_size)
preds = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(X_batch, w) + b)
correct_preds = tf.equal(tf.argmax(preds, 1), tf.argmax(Y_batch, 1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_sum(tf.cast(correct_preds, tf.float32))
total_correct_preds += sess.run(accuracy)
print "Accuracy {0}".format(total_correct_preds/MNIST.test.num_examples)